Atmospheric boundary layer (ABL)
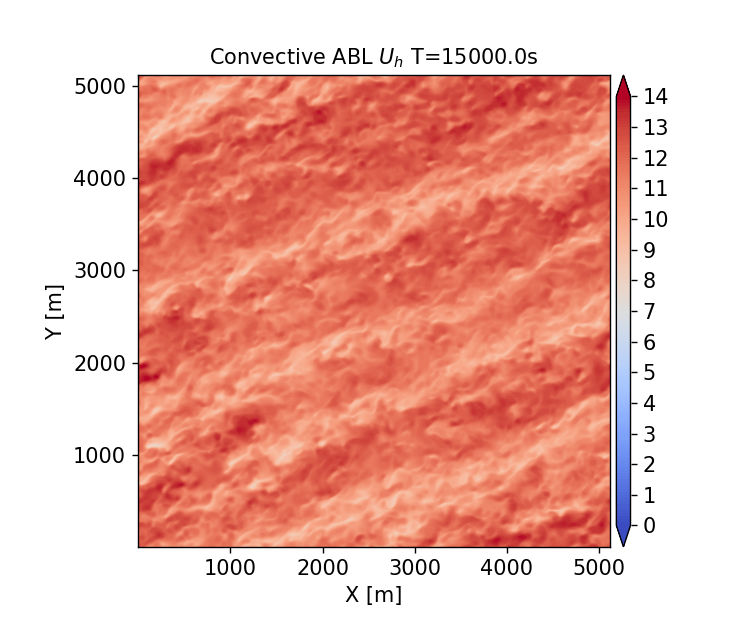
Two different atmospheric boundary simulations are documented here:
Neutral ABL: Simulations of the geostrophically forced neutral ABL from Berg et (2020).
Convectively unstable ABL: The precursor ABL flow used for the NREL5MW blade resolved and ALM studies.